Unveiling the mysteries of Earth’s geological processes, the Rock Cycle Gizmo Answer Key serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the dynamic transformation of rocks. Dive into the fascinating world of weathering, erosion, and deposition, and unravel the intricate interplay of factors that shape our planet’s rocky tapestry.
Delving deeper, we’ll explore the diverse rock types represented in the Gizmo, from igneous to sedimentary and metamorphic. Discover how these rocks evolve through the relentless forces of nature, transitioning from one form to another in an endless cycle of creation and renewal.
Rock Cycle Gizmo Overview
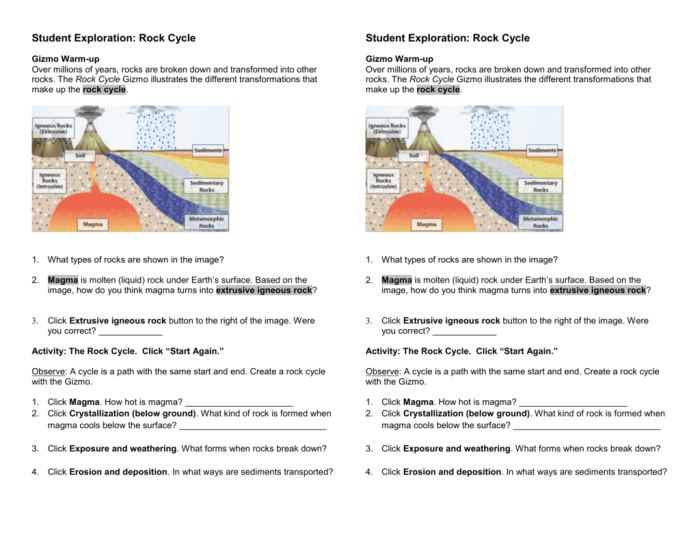
The Rock Cycle Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows students to explore the processes involved in the rock cycle. The Gizmo features a variety of rock types, including igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Students can use the Gizmo to create their own rock formations and observe how they change over time.
The Rock Cycle Gizmo is a valuable tool for teaching students about the rock cycle. The Gizmo can help students to understand the different types of rocks, the processes involved in the rock cycle, and the importance of the rock cycle in the Earth’s system.
Different Rock Types Represented in the Gizmo, Rock cycle gizmo answer key
The Rock Cycle Gizmo includes a variety of rock types, including:
- Igneous rocks: Igneous rocks are formed when magma or lava cools and solidifies. Igneous rocks can be classified into two main types: extrusive igneous rocks and intrusive igneous rocks. Extrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma or lava cools and solidifies on the Earth’s surface.
Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma or lava cools and solidifies beneath the Earth’s surface.
- Sedimentary rocks: Sedimentary rocks are formed when sediments are compacted and cemented together. Sediments are pieces of rock, mineral, or organic matter that have been transported by wind, water, or ice. Sedimentary rocks can be classified into two main types: clastic sedimentary rocks and chemical sedimentary rocks.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed when sediments are compacted and cemented together. Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed when minerals precipitate out of water.
- Metamorphic rocks: Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions. Metamorphic rocks can be classified into two main types: foliated metamorphic rocks and non-foliated metamorphic rocks. Foliated metamorphic rocks have a layered or banded appearance.
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks do not have a layered or banded appearance.
Processes of the Rock Cycle
The rock cycle is a continuous process that transforms rocks from one type to another. It involves three main processes: weathering, erosion, and deposition.
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller pieces. This can be caused by physical processes, such as freezing and thawing, or by chemical processes, such as oxidation. Erosion is the process of transporting weathered rocks from one place to another.
This can be caused by water, wind, or ice. Deposition is the process of depositing eroded rocks in a new location. This can occur when the transporting agent slows down or stops, or when the rocks become too heavy to be carried further.
Weathering
Weathering is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller pieces. This can be caused by physical processes, such as freezing and thawing, or by chemical processes, such as oxidation. Physical weathering occurs when rocks are exposed to extreme temperatures, causing them to expand and contract.
This can cause the rocks to crack and break down. Chemical weathering occurs when rocks are exposed to water and air, which can cause them to dissolve or oxidize.
Erosion
Erosion is the process of transporting weathered rocks from one place to another. This can be caused by water, wind, or ice. Water erosion occurs when water flows over rocks, carrying away small pieces of rock. Wind erosion occurs when wind blows over rocks, carrying away small particles of rock.
Ice erosion occurs when glaciers or ice sheets move over rocks, scraping away the surface of the rocks.
Deposition
Deposition is the process of depositing eroded rocks in a new location. This can occur when the transporting agent slows down or stops, or when the rocks become too heavy to be carried further. When the transporting agent slows down or stops, the rocks will settle out of the water or wind and be deposited on the ground.
When the rocks become too heavy to be carried further, they will be deposited on the ground.
Factors Influencing the Rock Cycle
The rate and direction of the rock cycle are influenced by various factors, including temperature, pressure, and water.
Temperature and pressure are the main factors that determine the type of rock that forms. For example, high temperature and pressure can cause minerals to recrystallize, forming metamorphic rocks. On the other hand, low temperature and pressure can cause minerals to precipitate out of solution, forming sedimentary rocks.
The rock cycle gizmo answer key is an excellent resource for understanding the processes that shape the Earth’s crust. If you’re looking for a captivating read to complement your studies, I highly recommend checking out the thorny trap of love novel . Its intricate plot and relatable characters will keep you engrossed from start to finish.
Afterward, return to the rock cycle gizmo answer key to reinforce your understanding of Earth’s dynamic geological processes.
Water
Water is another important factor that influences the rock cycle. Water can dissolve minerals, transport them, and deposit them in new locations. This can lead to the formation of sedimentary rocks, such as limestone and sandstone. Water can also cause rocks to weather, which is the process of breaking down rocks into smaller pieces.
Examples of Rock Cycle Transformations: Rock Cycle Gizmo Answer Key
The rock cycle is a continuous process that transforms rocks from one type to another. These transformations can occur through various geological processes, including weathering, erosion, deposition, metamorphism, and igneous activity.
The following table provides examples of how different rock types are formed and transformed through the rock cycle:
| Original Rock Type | Transformation Process | New Rock Type |
|---|---|---|
| Igneous rock | Weathering and erosion | Sedimentary rock |
| Sedimentary rock | Metamorphism | Metamorphic rock |
| Metamorphic rock | Melting | Igneous rock |
Applications of the Rock Cycle
Understanding the rock cycle has practical applications in various fields, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making.
Knowledge of the rock cycle is essential for geological surveys, as it helps geologists identify and map different rock formations, understand their origins, and predict the presence of valuable mineral resources. This information is crucial for resource exploration and sustainable mining operations.
Mining Operations
- Exploration:The rock cycle provides a framework for understanding the formation and distribution of ore deposits, guiding exploration efforts to target areas with high potential for mineral extraction.
- Extraction:Knowledge of the rock cycle helps miners determine the most efficient and environmentally responsible methods for extracting minerals, considering factors such as rock type, mineral composition, and geological structures.
- Waste Management:Understanding the rock cycle enables miners to develop strategies for managing waste materials generated during mining operations, minimizing environmental impacts and promoting sustainable practices.
Environmental Conservation
- Land Use Planning:The rock cycle informs land use planning decisions by providing insights into the geological stability, soil quality, and water resources of an area. This knowledge helps planners make informed choices about land use, minimizing risks associated with geological hazards and protecting sensitive ecosystems.
- Water Management:Understanding the rock cycle is crucial for managing water resources. It helps identify aquifers, assess groundwater quality, and predict the impact of human activities on water availability and quality.
- Erosion Control:The rock cycle provides insights into the processes that contribute to soil erosion and weathering. This knowledge enables the development of effective erosion control measures, preserving soil health and protecting ecosystems.
FAQ Insights
What is the purpose of the Rock Cycle Gizmo?
The Rock Cycle Gizmo is an interactive simulation that allows students to explore the processes and factors involved in the rock cycle.
What are the three main processes of the rock cycle?
The three main processes of the rock cycle are weathering, erosion, and deposition.
How do temperature and pressure influence rock formation?
Temperature and pressure can affect the type of rock that forms. For example, high temperature and pressure can cause rocks to metamorphose into new types of rocks.