Delving into the realm of chemistry, the element compound mixture worksheet answer key serves as an indispensable guide, unlocking the intricacies of matter’s composition. This comprehensive resource elucidates the fundamental differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures, empowering learners to decipher the building blocks of our world.
As we embark on this scientific expedition, we will delve into the unique properties that distinguish these substances, unraveling the secrets behind their physical and chemical characteristics. Moreover, we will explore the practical applications of these principles, showcasing how they shape our understanding of the world around us.
1. Introduction
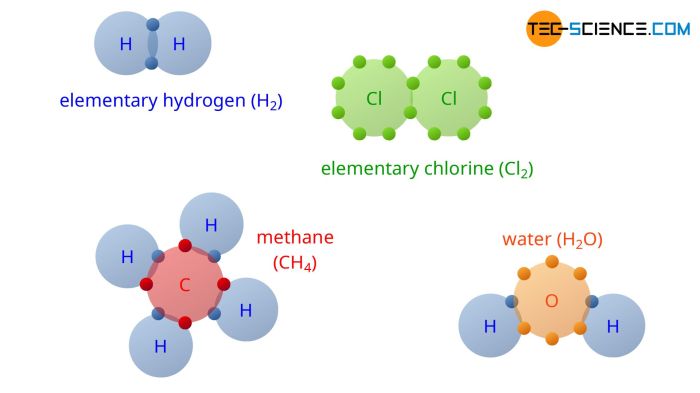
Matter can be classified into three categories: elements, compounds, and mixtures. Elements are the simplest form of matter and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Compounds are made up of two or more elements that are chemically combined.
Mixtures are combinations of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically combined.
Here are some examples of elements, compounds, and mixtures:
- Elements: hydrogen, oxygen, gold, silver
- Compounds: water (H 2O), salt (NaCl), sugar (C 12H 22O 11)
- Mixtures: air (a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases), seawater (a mixture of water and salt), sand (a mixture of different minerals)
2. Properties of Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Physical Properties, Element compound mixture worksheet answer key
The physical properties of elements, compounds, and mixtures can be used to identify them. Some of the most common physical properties include:
- Color: Elements, compounds, and mixtures can have different colors. For example, gold is a yellow metal, water is colorless, and blood is red.
- Odor: Elements, compounds, and mixtures can have different odors. For example, sulfur has a strong, unpleasant odor, while vanilla has a sweet, pleasant odor.
- Taste: Elements, compounds, and mixtures can have different tastes. For example, salt is salty, sugar is sweet, and vinegar is sour.
- Melting point: The melting point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a solid to a liquid. Different substances have different melting points. For example, water melts at 0°C, while gold melts at 1064°C.
- Boiling point: The boiling point is the temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid to a gas. Different substances have different boiling points. For example, water boils at 100°C, while alcohol boils at 78°C.
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of elements, compounds, and mixtures can also be used to identify them. Some of the most common chemical properties include:
- Reactivity: The reactivity of a substance is its tendency to react with other substances. Some substances are very reactive, while others are relatively inert. For example, sodium is a very reactive metal that reacts easily with water, while gold is a relatively inert metal that does not react easily with other substances.
- Flammability: The flammability of a substance is its tendency to burn. Some substances are very flammable, while others are not flammable at all. For example, gasoline is a very flammable liquid, while water is not flammable.
- Acidity: The acidity of a substance is its tendency to donate protons (H+ ions). Some substances are acidic, while others are basic or neutral. For example, hydrochloric acid is a strong acid, while sodium hydroxide is a strong base.
3. Separation of Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
There are a variety of methods that can be used to separate elements, compounds, and mixtures. Some of the most common methods include:
- Filtration: Filtration is a method of separating solids from liquids. A filter paper is used to trap the solids, while the liquid passes through. Filtration can be used to separate sand from water, for example.
- Distillation: Distillation is a method of separating liquids from solids or from other liquids. The mixture is heated, and the different components vaporize at different temperatures. The vapors are then condensed and collected. Distillation can be used to separate water from salt water, for example.
- Chromatography: Chromatography is a method of separating different components of a mixture based on their different rates of movement through a stationary phase. Chromatography can be used to separate dyes, for example.
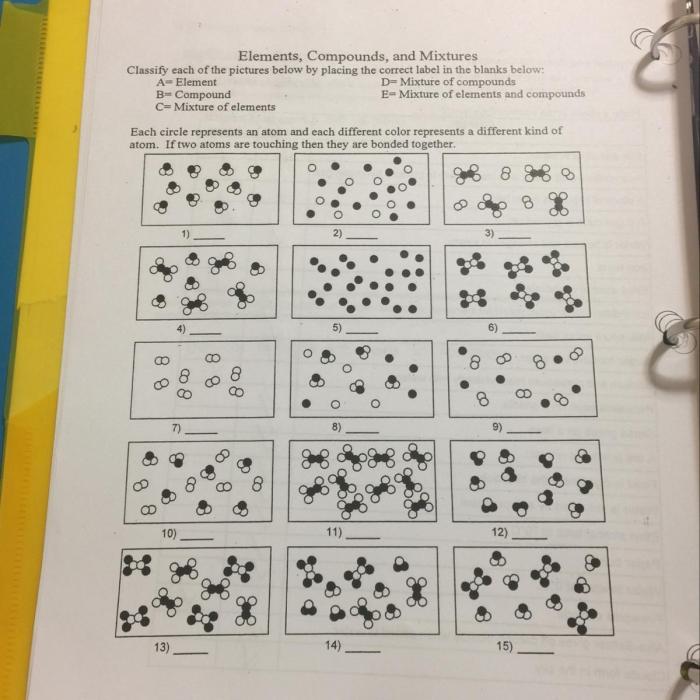
4. Worksheet Answer Key
Question 1:What is the difference between an element, a compound, and a mixture?
Answer:An element is the simplest form of matter and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. A compound is made up of two or more elements that are chemically combined. A mixture is a combination of two or more elements or compounds that are not chemically combined.
Question 2:Give an example of an element, a compound, and a mixture.
Answer:Element: gold; Compound: water; Mixture: air
Question 3:What are some of the physical properties that can be used to identify elements, compounds, and mixtures?
Answer:Color, odor, taste, melting point, and boiling point
Question 4:What are some of the chemical properties that can be used to identify elements, compounds, and mixtures?
Answer:Reactivity, flammability, and acidity
Question 5:Describe three methods that can be used to separate elements, compounds, and mixtures.
Answer:Filtration, distillation, and chromatography
Expert Answers: Element Compound Mixture Worksheet Answer Key
What is the primary distinction between an element and a compound?
Elements are pure substances composed of a single type of atom, while compounds are substances formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in fixed proportions.
How can we differentiate between a compound and a mixture?
Compounds exhibit a definite composition and cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical means, whereas mixtures retain the properties of their individual components and can be separated by physical methods.